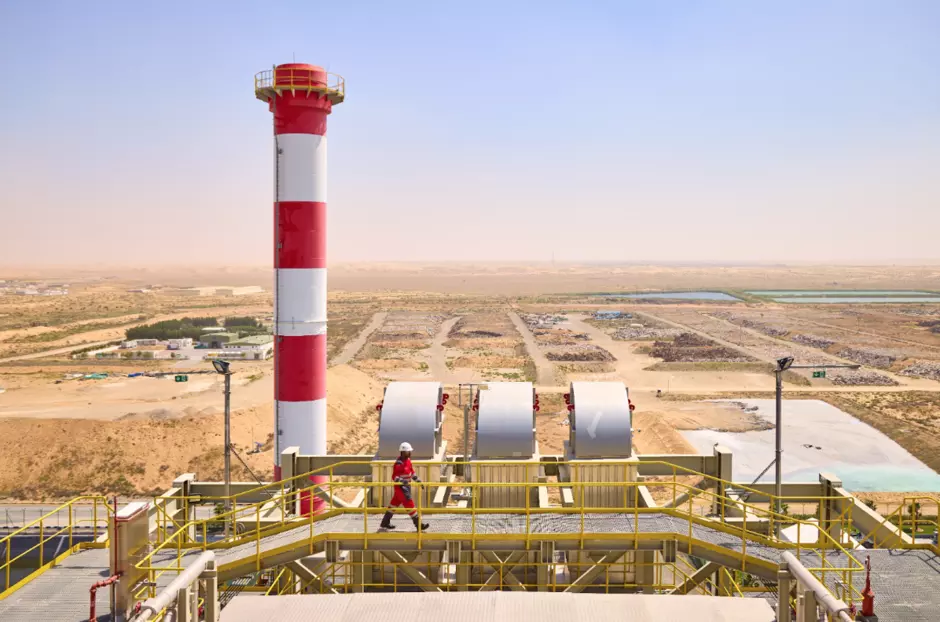
The Challenge
Municipal Solid Waste Incineration in the Middle East faces a complex array of challenges across multiple dimensions.
Operationally, the region struggles with high moisture content waste, insufficient segregation practices, and varying waste composition that affects combustion efficiency. Technical challenges include equipment durability issues in the harsh climate, maintenance difficulties in dusty environments, and the need for sophisticated emissions control systems. Economic barriers are significant, including high capital and operational costs, competition from cheaper disposal methods, and difficulties in securing consistent waste supply contracts. Environmental concerns center around emissions control and high energy consumption for cooling systems. The situation is further complicated by yet to be developed regulatory frameworks, limited technical expertise, and cultural barriers to waste management. Public resistance, limited regional experience with waste-to-energy technologies, and infrastructure limitations for energy distribution add additional layers of complexity to implementing successful municipal incineration projects in the region.
Solutions
Solid Waste Incineration in the Middle East represents a growing waste management solution that addresses increasing urbanization and waste generation challenges.
The technology involves thermal treatment of municipal solid waste to reduce volume and generate energy, while adhering to strict environmental standards. Key features include advanced emissions control systems, energy recovery capabilities, and sophisticated waste processing technologies. These facilities typically incorporate modern technologies for efficient combustion, air pollution control, and energy recovery, while being adapted to handle the region's specific waste characteristics and climate conditions. The implementation of such facilities helps reduce landfill dependency while contributing to the region's renewable energy goals.
Combined Heat and Power(CHP) Incineration Plants
Veolia operates CHP waste-to-energy facilities that incinerate municipal solid waste to simultaneously produce electricity and heat. High-efficiency boilers convert thermal energy from combustion into steam, which powers turbines and provides district heating. These systems maximize energy recovery from non-recyclable waste while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and supporting urban heating networks in line with circular economy and decarbonization goals.
Flue Gas Treatment and Emission Control
Veolia ensures environmental compliance in its incineration plants through advanced flue gas treatment systems. Technologies such as selective catalytic reduction (SCR), electrostatic precipitators, and activated carbon injection remove pollutants including dioxins, NOx, heavy metals, and acid gases. This minimizes environmental impact and ensures emissions remain well below regulatory limits, making municipal waste incineration cleaner, safer, and more sustainable.
Bottom Ash Recovery and Material Valorization After incineration
Veolia recovers bottom ash—residual material left after combustion—for recycling. Metals such as steel and aluminum are extracted using magnets and eddy current separators. The remaining mineral fraction is processed for use in construction materials, such as road base layers. This approach diverts waste from landfills, recovers valuable resources, and supports sustainable materials management in the waste-to-energy cycle.
Waste Pre-Treatment and Feedstock
Waste Pre-Treatment and Feedstock OptimizationTo improve combustion efficiency and energy yield, Veolia pre-treats municipal waste before incineration. This includes removing recyclables, drying high-moisture waste, and shredding bulky items. Feedstock optimization ensures consistent calorific value, reduces emissions, and enhances plant performance. This pre-treatment process is crucial for maintaining stable incineration conditions and maximizing the energy recovery potential of mixed municipal waste.

Veolia's municipal solid waste incineration solutions combine advanced waste-to-energy technology with sophisticated environmental controls, converting waste into valuable energy through efficient heat recovery and power generation.
Our integrated approach features smart automation, continuous monitoring, and comprehensive safety systems, while delivering significant waste volume reduction and greenhouse gas mitigation. This approach ensures optimal resource recovery and environmental compliance while providing sustainable energy solutions for regional needs.
Feature
details
Overmillion tons annual processing
million tonnes of Industrial waste handled
OverMW power generation
M tons CO2 avoided
Operate household waste incineration plants
Key
figures
Benefits & Value Proposition
Emissions control
Advanced flue gas treatment systems at Veolia incineration plants remove harmful pollutants, ensuring emissions remain well below legal limits and safeguarding air quality and public health in surrounding communities.

Resource recovery
Veolia extracts metals from incineration ash for recycling and reuses the remaining mineral content in construction, promoting circular economy practices and reducing demand for virgin raw materials.

Energy recovery
Veolia transforms non-recyclable municipal waste into electricity and heat, supplying power to homes and businesses while reducing reliance on fossil fuels and supporting a more sustainable energy infrastructure.
Landfill Diversion
Incineration significantly reduces waste volume, minimizing the need for landfills. This helps conserve land, reduce methane emissions, and prevent long-term environmental contamination from buried municipal waste.
Case studies
Discover the experiences of different players in our region









